There are few things in life that make summer more bearable than your air conditioner. Isn’t it amazing that such a simple device can improve your quality of life, whether in your home or office?
But have you ever thought about how your air conditioner works?
As we roll into summer, your friends at ASI are here to walk you through the basics and provide some helpful tips for improving efficiency and getting the most out of your unit.
Air Conditioner Background History
The first air conditioner was invented in 1902 by Willis Carrier, who wanted to cool the printing plant he worked for. He realized the process of evaporating water into the air could be used to cool down large rooms and developed the first modern air conditioner. Although, back then, the units were incredibly bulky and expensive, making them inaccessible to the masses. It wasn’t until the 1950s that air conditioning became a common feature in homes and businesses.
Types of Air Conditioner Units
Central Air Conditioners
Central air conditioners are one of the most common types of air conditioners. These units use an outdoor unit to cool the entire home or business. They are energy efficient and even provide cooling throughout the building but require ducting for installation.
Cassette Air Conditioners
Cassette air conditioners are ceiling-mounted units that provide cooling to larger spaces. They are ideal for applications where central air conditioners are impractical, such as large warehouses or garages.
Ductless Mini-Split Air Conditioners
Ductless mini-split air conditioning systems offer a revolutionary alternative to traditional central AC. Unlike their centralized counterparts, these independent units don’t require any ducting for installation and can be conveniently mounted on wall surfaces in each room of the house.
Commercial Air Conditioners
Commercial air conditioners are the powerful solution for heavy-duty cooling needs in larger buildings. From multi-story offices and factories to stores, these units provide superior performance that can keep occupants comforted year-round.
Window Air Conditioners
Window air conditioners offer an ideal cooling solution for homes or apartments with tight space restrictions. As the name suggests, these units are installed in windows and their cooling effectiveness is isolated to smaller areas.
Split Air Conditioners
Split air conditioners are composed of two distinct parts: the indoor unit and the outdoor unit. The interior portion is mounted on an internal wall, distributing chilled air throughout the space with a fan while its external counterpart hosts the compressor and condenser. Compared to window units, split systems tend to be more robust in power but provide consistent cooling as well.
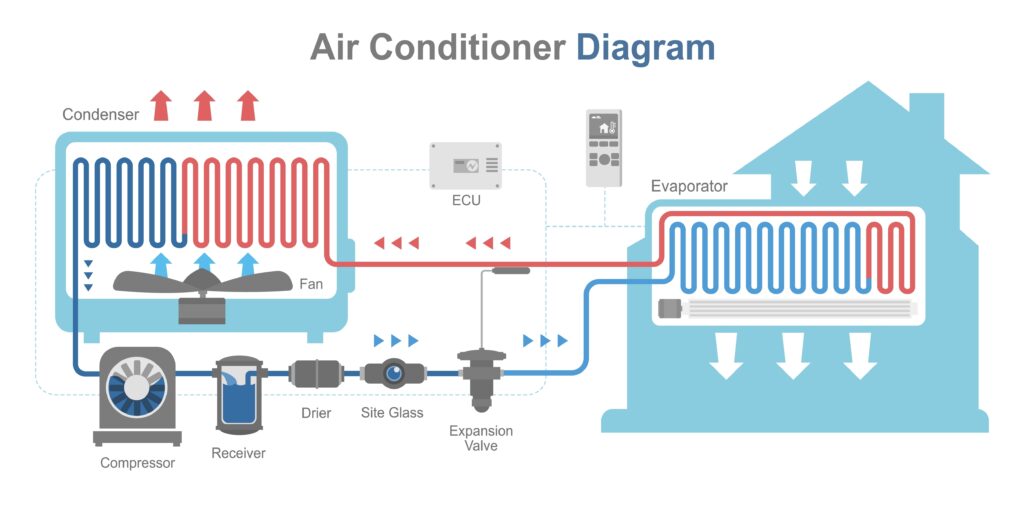
Air Conditioner Parts
If you’ve never seen the inside of an air conditioner, you might be taken aback by all the different pieces and parts. Though, most air conditioners use a combination of the same basic components. The most critical parts of its operation are as follows:
Evaporator Coil
The evaporator coil is the component that absorbs heat from the indoor air. The cold refrigerant inside it causes the indoor air’s temperature to drop, which then circulates through your space.
Compressor
The compressor is part of an air conditioner that compresses and pumps the refrigerant through its system. It works by taking warm air from the indoor unit, cooling it down, and pushing it back into your space.
Condenser Coil
The condenser coil is part of an air conditioner that releases heat from the refrigerant. This is part of the system that dissipates the heat from your home or business, making it a crucial component in its overall operation.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve is a small device that helps regulate refrigerant flow in and out of the system. It works by controlling the pressure of the refrigerant, so it can pass through all the necessary components without issue.
Air Conditioning Cooling Cycle: Step by Step
To achieve a comfortable indoor temperature, air conditioners must undergo an intricate process of cooling.
The system begins with the compressor drawing warm air from inside and compressing it to raise its temperature. This heated air is then piped outside through the condenser coil where heat can be released into nature’s environment before being pushed via an expansion valve, which reduces pressure, further cooling down refrigerant. It goes on to reach the evaporator coil that absorbs any residual warmth in your home while delivering a cooled-down atmosphere back indoors until an established temperature is reached.
Efficient AC Usage: Don’t Work Your AC Into Exhaustion!
To ensure you’re getting the most out of your air conditioner, it’s important to use it correctly. The last thing you want to do is to run your AC so hard it works less efficiently: or worse, breaks down completely!
Here are a few tips for better energy efficiency:
- Ensure your unit is correctly sized for the space you need to cool.
- Take advantage of ceiling fans and other ventilation systems to reduce strain on your AC.
- Close and seal off unused rooms so your air conditioner isn’t overworking itself.
- Replace the air filter regularly to ensure maximum efficiency.
- Keep outdoor units free from debris and obstructions for better airflow.
- Use a programmable thermostat to keep energy costs low during peak times.
Air Conditioning Maintenance
Qualified HVAC technicians like ASI can help you with any repairs or cleaning that need to be done, as well as provide advice on how to keep your air conditioner running at its best. We’ll also help you check for any potential signs of trouble so that you can address them before they become a major problem.
Keep Cool. Call ASI.
Keep your AC running strong all summer long. Call and schedule your appointment with ASI today.